With the right ingredients, industrial mixer and packaging, you can establish your own toothpaste company. Here’s how toothpaste is made in a factory.
Do you ever wonder how your toothpaste, that daily dental essential, is created? The answer may surprise you. Let’s dive into the intriguing world of toothpaste production and uncover the secrets behind its magical properties.

Key Takeaways:
- Discover the fascinating journey of toothpaste from ancient remedies to modern dental magic.
- Learn about the main ingredients that go into toothpaste and their crucial roles, including how advanced mixers play a vital role in the production process.
- Explore the high-tech manufacturing process that transforms raw materials into the toothpaste you use daily, with a focus on the significant contribution of industrial mixers.
History of Toothpaste: From Myrrh to Mint
Ancient Tooth-Cleaning Methods

From the dawn of civilization, humans have sought ways to clean their teeth and maintain oral hygiene. The ancient Egyptians concocted mixtures of green lead, verdigris, and incense, while early Chinese populations ground fish bones for dental maintenance. In the Middle Ages, sand and pumice were used by Arabs, though their harshness on enamel was noted. Western cultures, on the other hand, experimented with strong acids and even table salt as tooth cleaners.
The Birth of Modern Toothpaste
The transformation of tooth-cleaning practices came in the mid-19th century when Dr. Washington Wentworth Sheffield, a dental surgeon and chemist, introduced the world to the first toothpaste. This innovative “Creme Dentifrice” soon found its way into households. Sheffield’s invention marked the beginning of a revolution in dental care.
Ingredients in Modern Toothpaste: The Dental Trio
1. The Role of Abrasives
Abrasives are the unsung heroes of toothpaste, making up between 8 and 20% of the formula. They work diligently to polish your teeth, helping to remove the stubborn plaque that can accumulate over time. So, next time you brush, remember that abrasives are your secret weapon against that “fuzzy” feeling.
2. Fluoride’s Fight Against Cavities
Fluoride, a well-known toothpaste ingredient, plays a crucial role in preventing cavities and aiding in the formation of dental enamel. The fluoride content can vary across the globe, but its impact on dental health is consistent. So, when you brush, you’re not just cleaning; you’re fortifying your teeth.
3. The Foaming Action of Detergents
Ever wondered why toothpaste foams in your mouth? The answer lies in detergents or surfactants like sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS). These compounds help distribute the paste effectively while providing antimicrobial benefits. That satisfying foam is your indicator that your toothpaste is doing its job.
Toothpaste Manufacturing: Turning Ingredients into Tubes
From Silos to Silky Paste

Toothpaste production is a well-oiled, high-tech process. It begins with sourcing and quality-testing ingredients before they’re weighed and combined. Careful attention is paid to temperature and humidity to ensure perfect mixing. The toothpaste mix, akin to a dental symphony, comes together in large vats. These vats are integral in creating the consistency and quality you expect.
The Art of Tube Filling

Toothpaste tubes are prepared with precision and cleaned to perfection, ensuring dust and particles are a thing of the past. The tube tops are sealed, and the bottoms are left open, ready for filling. A specialized machine handles the task of pairing the silky paste with the waiting tubes.
The Final Touch: Branding and Packaging
The process concludes with the marked-filled tubes bearing the stamp of their birthplace and date. Then they undergo one last round of quality checks before they’re sealed in boxes and shipped to their destinations. The next time you pick up a toothpaste tube from the shelf, remember the meticulous journey it underwent to reach your bathroom.
Toothpaste Manufacturing Equipment
1. Raw Materials and Ingredient Handling:
- Silos: Used for bulk storage of raw materials and ingredients.
- Weighing Equipment: Both manual and mechanical weighing equipment for precise measurement of ingredients.
2. Mixing Process
- Stainless Steel Mixing Vats: Large vats with temperature and humidity control for blending the toothpaste ingredients.
3. Filling and Sealing
- Blowers and Vacuum Systems: Used to clean toothpaste tubes before filling by removing dust and particles.
- Filling Machines: Specialized machines for pumping toothpaste into individual tubes.
- Nozzles for Stripe Addition: Equipment with separate nozzles for adding colored stripes to toothpaste.
- Stamping Equipment: Used to stamp toothpaste tubes with manufacturing information.
- Conveyor Belts: Transport toothpaste tubes between various stages, including filling and labeling.
4. Labeling and Branding
- Labeling Machines: Machines for labeling toothpaste tubes with essential information.
- Barcoding Systems: Used for tracking ingredients, batches, and ensuring traceability.
5. Packaging
- Packaging Machines: Machines for placing filled toothpaste tubes into individual paperboard boxes.
- Master Cartons: Larger cartons for containing multiple boxes of toothpaste tubes for distribution and storage.
Problems in Toothpaste Mixing/Production:
- Consistency and Homogeneity: Achieving the right consistency and uniform distribution of ingredients is crucial in toothpaste production. Inconsistent mixing can lead to quality issues, affecting the effectiveness of the toothpaste.
- Efficient Dispersion: Ensuring that abrasive particles, flavors, and other ingredients are effectively dispersed in the toothpaste mixture can be a challenge. Inefficient dispersion may result in clumps or inconsistent texture.
The Solution: Advanced Toothpaste Mixing with Ginhong Mixers
Addressing the unique challenges in toothpaste production requires the exceptional capabilities of Ginhong Mixers, a cutting-edge solution that not only overcomes these issues but also optimizes the entire manufacturing process:
Stage 1: Mixing Precision
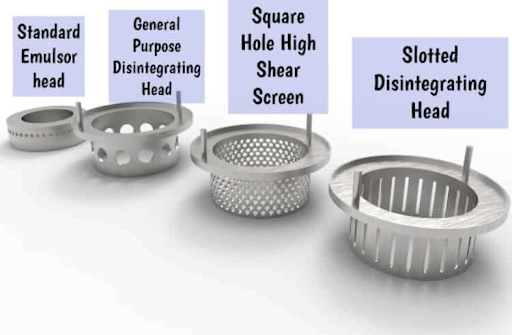
The journey begins with mixers, where the vessel is filled with water, and the mixer is set into motion. Powdered ingredients are gently introduced into the system. Ginhong Mixers utilize their high-speed rotation to create a powerful suction force, efficiently drawing both liquid and powders into the workhead. Within the workhead, the materials undergo intense shear forces, ensuring even distribution and consistent blending.
Stage 2: Agglomerate Disintegration
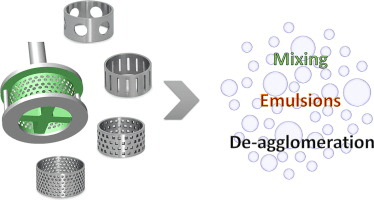
The process continues as agglomerates are expertly disintegrated between the rotor blades and the stator wall. The product is then propelled through the stator, rejoining the mix. Simultaneously, fresh materials are seamlessly drawn into the workhead, perpetuating the mixing cycle. This continuous mixing pattern guarantees rapid and complete hydration of thickening agents, essential for achieving the desired toothpaste consistency.
Stage 3: Dispersing Key Ingredients
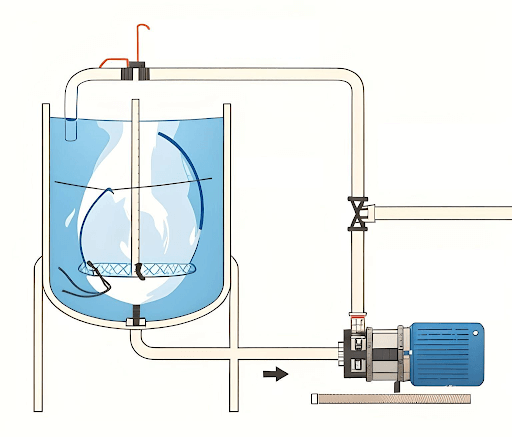
In the final crucial step, essential ingredients are introduced and dispersed in a similar manner. This meticulous process results in a homogeneous mixture of toothpaste, quickly achieved while maintaining the product’s desired texture and quality.
Ginhong Mixers play a pivotal role in toothpaste production, overcoming common challenges and ensuring a consistently high-quality end product. Their precision mixing capabilities contribute to the uniform distribution of ingredients, from abrasives to flavors, and facilitate the creation of toothpaste with the desired properties.
Ginhong Toothpaste Mixing Equipment Product Range
Selecting the right industrial mixer for toothpaste production depends on various factors, including batch size, ingredient formulation, and the desired toothpaste viscosity. Ginhong offers a diverse range of mixing equipment tailored to meet your specific toothpaste processing needs:
1. High Shear Batch Mixers

Ideal for small to large-sized toothpaste batches, typically ranging up to 30 to 6,000 L. These mixers are suitable for the production of various toothpaste formulations and come with the added convenience of working with a variety of mixing tanks. It is suitable for mixing cream and toothpaste emulsions ranging from 20,000 – 80,000cps viscosity.
2. High Shear In-Line Mixers

When dealing with larger toothpaste batches, Ginhong offers efficient in-line mixers that can be easily integrated into your production setup. These mixers facilitate uniform dispersion of ingredients, ensuring toothpaste consistency while minimizing aeration. It’s suitable for processing a variety of high viscous cream, lotion, ointment, toothpaste and other emulsions of 5,000 – 100,000cps viscosity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Toothpaste
1. How is toothpaste made?
Toothpaste is made through a meticulous manufacturing process that involves sourcing raw materials, blending them in mixing vats, filling toothpaste tubes, and packaging the final product. To get a detailed understanding, explore the earlier sections of this article on the “Toothpaste Manufacturing Process.”
2. Who invented toothpaste?
Toothpaste, in its modern form, was introduced by Dr. Washington Wentworth Sheffield, a dental surgeon and chemist, in the mid-19th century. Discover more about the history of toothpaste in the “Birth of Modern Toothpaste” section.
3. What is toothpaste made of?
Toothpaste is composed of various ingredients, including abrasives, fluoride, and foaming agents, which play crucial roles in maintaining oral hygiene. Delve into the “Ingredients in Modern Toothpaste: The Dental Trio” section to learn more about these components.
4. Where is Colgate toothpaste made?
Colgate, one of the renowned toothpaste brands, has manufacturing facilities worldwide. You can check the packaging or visit Colgate’s official website for specific information on the production location of their toothpaste products.
5. When was toothpaste made?
The history of toothpaste dates back to ancient times when various cultures used different materials for oral hygiene. In its modern form, toothpaste was invented in the 19th century by Dr. Sheffield. Explore the historical journey in the “History of Toothpaste: From Myrrh to Mint” section.
6. Is toothpaste made of bones?
No, modern toothpaste is not made of bones. In the past, some cultures used ingredients like ground fish bones for dental maintenance, but today’s toothpaste comprises a combination of safe and effective components. Refer to the “Ingredients in Modern Toothpaste: The Dental Trio” section for insights into modern toothpaste ingredients.
7. What is the raw material in toothpaste?
Raw materials used in toothpaste production include abrasives, binders, humectants, flavors, fluoride, and water. Find a detailed discussion on these raw materials in the “Toothpaste Manufacturing Equipment” section.
8. How are stripes in toothpaste made?
Creating stripes in toothpaste is a fascinating process. During production, after the toothpaste mixture is prepared and before it’s filled into the tubes, specialized filling machines come into play. These machines are equipped with three or four nozzles designed to inject different-colored stripes into the toothpaste simultaneously.
This meticulous process ensures that the colorful stripes are evenly distributed within the toothpaste, giving it that distinctive and appealing appearance.
Once the stripes are added, the toothpaste is ready to be filled into tubes, crimped, and eventually packaged for distribution. The addition of stripes is a unique and eye-catching feature that has become increasingly popular among toothpaste varieties.
Conclusion
The journey of toothpaste from ancient remedies to modern dental marvels is both fascinating and intricate. The next time you squeeze that tube, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for the magic it brings to your daily dental routine.
Ginhong Mixers serve as indispensable tools in toothpaste manufacturing, addressing common production challenges, enhancing product quality, and streamlining the production process. Ginhong’s expertise as an industrial mixer manufacturer and supplier ensures that you have access to top-of-the-line equipment for your toothpaste production needs.
