From mixing equipment to the manufacturing process, this article presents the Syrup Manufacturing Process and how syrup is made in a factory.
Syrups are concentrated liquid solutions with a multitude of applications, from cough syrups and sugar syrups to pharmaceutical syrups. Their versatility makes them a vital component in various industries, including medicine, food, and beverages.
Key Takeaways:
- Understand the key steps in syrup manufacturing.
- Learn about the equipment used in syrup production.
- Explore the different types of syrups and their manufacturing processes.
- Gain insights into the factors affecting syrup quality.
Where is Syrup Made?

Syrup manufacturing facilities are commonly found in regions with access to raw materials and production resources. Geographical location plays a significant role in the availability of ingredients and the overall manufacturing process.
- Raw Material: These facilities cozy up to the sources of their main ingredients, like sugar. Being close to sugar refineries means a steady supply and less transportation fuss, which can save both time and money.
- Quality Quest: They pick spots where top-notch ingredients grow. After all, better ingredients lead to better syrups. Being where premium ingredients are abundant ensures syrup superiority.
- Resource Ready: Making syrup is like orchestrating a grand symphony; it takes energy, water, and a bunch of equipment. Facilities in regions with these resources readily available keep the syrup-making show running smoothly.
- Green Syrup Secrets: Some locations offer cleaner energy sources, which align with the syrup industry’s eco-friendly aspirations. It’s like syrup-making with a green twist, helping reduce the environmental footprint.
- Distribution: Syrup-making hubs are often close to big distribution centers. This means that your favorite syrups can hop onto distribution trucks and reach your pantry faster.
Types of Syrups and Their Uses

Syrups come in various types, each designed for a specific purpose. These include cough syrups, sugar syrups, and pharmaceutical syrups. Cough syrups help alleviate discomfort caused by respiratory issues, sugar syrups serve as sweeteners and bases for beverages, and pharmaceutical syrups deliver medication in a liquid form.
Here are some of the most common cough syrups:
|
|
|
Ingredients Used in Syrup Manufacturing
The core ingredients of syrups typically include sugars, sweeteners, and active ingredients. These components play a crucial role in defining the flavor, texture, and therapeutic properties of the final product.
Chesty Coughs Ingredients
- A chesty cough is a result of too much mucus being produced, which may be thick and difficult to cough up.
- Expectorants are active ingredients that help to break up any excess mucus that may have accumulated.
Dry Coughs Ingredients
- For a dry tickly cough, an over-the-counter medicine containing a cough suppressant to block the natural coughing reflex, such as pholcodine and dextromethorphan, should help.
Sugar Syrups Ingredients/Maple Syrup
Sweeteners and bases for beverages. Common applications include: Flavoring drinks, making cocktails, and desserts
Here’s a typical list of ingredients and percentages in the solution for cough syrups:
| Ingredients | Percentage | Function |
| Paracetamol | 2.5% | Active ingredient |
| Polyethylene Glycol | 10% | Solubilizer |
| Glycerin | 2.5% | Diluent and sweetener |
| Sucrose | 30% | Sweetening agent |
| Distilled Water | 20% | Diluent |
| Sweetener | 0.2% | Sweetener |
| Sodium Methyl Paraben | 0.150% | Preservative |
| Sodium Propyl Paraben | 0.03% | Preservative |
| Sodium Benzoate | 0.150% | Preservative |
| Citric Acid Monohydrate | 0.07% | pH modifier |
| Coloring Agent | 2.5% | Coloring agent |
| Flavor | 0.25% | Flavoring agent |
The Syrup Making Equipment

To produce high-quality syrups, specialized equipment is essential. Mixers, dissolvers, storage tanks, and filtering systems ensure the manufacturing process is efficient and the product meets industry standards.
The Syrup Manufacturing Process
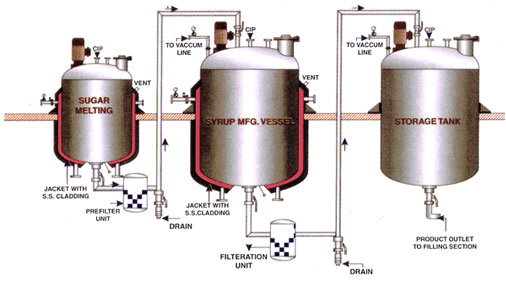
The syrup manufacturing process consists of several key steps, ensuring the final product is consistent, safe, and high in quality.
1. Sugar Preparation and Melting
Before manufacturing begins, sugar is graded, sieved, and transferred to a vessel to remove impurities. Distilled water is introduced and heated, creating a sugar-water solution. This melted sugar solution serves as the base for syrup production.
2. Mixing and Dissolution
In the mixing vessel, the sugar solution is vigorously mixed with other ingredients, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients or flavorings. The high-speed mixing, coupled with heat, efficiently disperses the ingredients into the solution, creating a homogeneous product.
3. Cooling and Filtering
After the initial mixing, the syrup undergoes cooling and filtering to remove impurities and maintain its quality. The filtration process ensures the syrup is free of unwanted particles and agglomerates.
4. Packaging and Quality Control
Once the syrup is ready, it is transferred into small bottles and undergoes a final quality control check. Packaging is essential to ensure the product reaches consumers in optimal condition.
Syrup Mixing Process
- Prior to mixing the ingredients, the preliminary steps are grading and sieving the sugar to remove impurities and unwanted particles from the ingredients.
- Then the partially cleaned sugar is transferred through vacuum to a vessel to melt it.
- Distilled water is introduced into the vessel with the sugar in it and heated, melting the sugar and producing a sugar water solution.
- The melted sugar will be filtered further, removing impurities, and then transferred into a manufacturing/main mixing vessel.
- In the mixing vessel, the pharmaceutical syrup is made by vigorously mixing the sugar water with other ingredients such as drugs, medicine powders, and vitamins.
- A cooling system cools the syrup transfer through an inline homogenizer and filter press for homogenized mixing and filtering up to 5 microns size in the storage tank.
- Post-processing of syrup is done before transferring it to small bottles and packing.
Factors Affecting Syrup Quality
Maintaining high-quality standards in syrup manufacturing is crucial. Challenges such as improper dissolution, varying viscosities, and equipment quality can affect the final product. Employing specialized equipment and rigorous quality control measures mitigates these challenges.
| Factors | Impact on Quality |
| Dissolution | Ensures even consistency |
| Viscosity | Affects the syrup’s texture |
| Equipment Quality | Influences production |
| Quality Control Measures | Ensures product consistency |
The Problem
Using conventional mixers and agitators for this process leads to several potential problems:
- The sugars are not properly dissolved to form the syrup.
- Hydration of powdered ingredients.
- Varying viscosities of ingredients and inefficient mixing systems lead to a non-uniform mixture and undissolved active ingredients.
- The end product is not smooth, agglomerate-free, and homogeneous.
- The equipment does not conform to GMP standards, which means that it doesn’t have self-cleaning features.
- High-energy heating is required to heat the sugar solution.
- Crystallization of the syrup can occur during heating/cooling.
- Heat can damage active ingredients.
The Solution
- When the mixing vessel is charged with the sugar-water solution and the powdered ingredients are added, the high-speed rotation of the rotor blades creates a powerful suction that draws liquid and solid ingredients into the workhead, mixing it thoroughly.
- An electric motor drives the shaft inside the mixing tank. This shaft is coupled with an impeller which it is rotated at a high speed, driving the sugar-water solution and powdered materials with strong centrifugal force. The mixer incorporates a high fluid shear inside the tank.
- The intake and expulsion of materials through the workhead ensures that the contents of the vessel pass many times through the workhead. The combination of heat, vigorous mixing, and particle size reduction accelerates the melting process of the ingredients and rapidly disperses the powder grinds into the sugar and water to produce a homogeneous end product.
- In this way, the syrup mixer rapidly disperses solids into liquids, hydrates the thickening and stabilizing agents, breaks down the remaining agglomerates, and finely reduces particle and globule size.
Advantages of Ginhong Syrup Mixer:
- Efficiency and Energy Savings: Ginhong’s mixer can produce 66% sucrose syrup at ambient temperatures, significantly saving energy while ensuring that the heat of dissolution is imparted in the form of shear. This not only benefits the environment but also your production costs.
- Consistency and Repeatability: Batch-to-batch product consistency and stability are paramount in pharmaceuticals. Ginhong’s mixer excels in maintaining these crucial factors, offering not only reliable quality but also high manufacturing savings.
- Texture and Quality: Ginhong’s mixer can create a uniformly mixed product, resulting in a smoother texture and better consistency in cough syrups. This ensures that each dose is as effective as the last.
- Agglomerate-Free Mixture: The mixer’s technology ensures that your mixture is agglomerate-free, avoiding clumps or inconsistencies in the final product.
- Reduced Waste and Sanitary Conditions: Ginhong’s mixer features a scraper that efficiently gathers material wastes without interrupting the production process. Moreover, the mixer and auxiliaries conform to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards and Cleaning-in-Place (CIP) regulations, ensuring sanitary and safe production.
These advantages make Ginhong’s cough syrup and liquid medicine mixer a valuable asset for pharmaceutical companies, ensuring high-quality, efficient, and environmentally friendly production of cough syrups.
Recommended Ginhong Syrup Mixing Equipment
1. Ginhong High Shear Mixers

- JX Lab Batch Homogenizer
- ZX Powder Liquid Mixer
- DX Bottom Entry Homogenizer
- ZX Inline Homogenizer
- FS High-Speed Disperser
2. Ginhong Vacuum Emulsifier Homogenizer
- RX Vacuum Homogenizer Mixer: Performing mixing under vacuum conditions, this mixer eliminates the unwanted effects of aeration, making it ideal for producing high-quality, bubble-free cough syrups.
- RS Vacuum Emulsifier Mixer: The RS Vacuum Emulsifier Mixer ensures that your cough syrup remains free from aeration, resulting in consistent and top-quality products.
Conclusion
Syrup manufacturing is a complex yet fascinating process that yields products essential in various industries. Understanding the steps involved, the specialized equipment used, and the factors affecting syrup quality is vital for both consumers and manufacturers. As the industry continues to innovate and grow, syrup production promises a brighter, more efficient future.

